A Simple Explanation for RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5 and RAID 10 with Diagrams

In this article, I’ll explain the main key points and differences between basic RAID systems. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks. This article will show you the minimum hardware requirements and the advantages of different RAID types “RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5 and RAID 10” . As a system engineer, you will face and deal with setting up some servers with RAID systems.
RAID can be implemented in two ways:
- Hardware RAID: If your server has a hardware raid controller on it, this type of RAID is controlled by the raid controller and you can connect to the controller when systems is booting from BIOS Menu.
- Software RAID: If your server does not has a hardware raid controller and you need to setup a raid systems, then you will setup a software raid, this type of raid is controlled from the Linux OS.
On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of RAID.
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0)
This article explains the main difference between these raid levels along with an easy to understand diagram.
In all the diagrams mentioned below:
- A, B, C, D, E and F – represents blocks
- p1, p2, and p3 – represents parity
RAID LEVEL 0
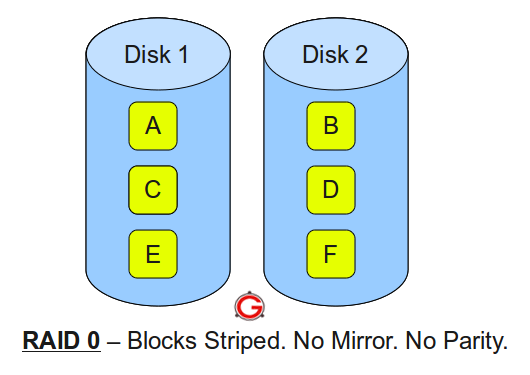
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 0:
- Minimum 2 disks.
- Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped ).
- No redundancy ( no mirror, no parity ).
- Don’t use this for any critical system.
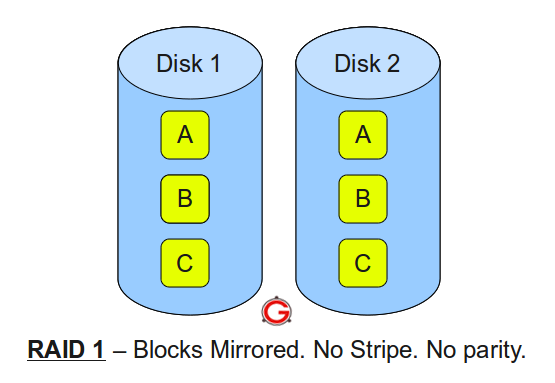
RAID LEVEL 1
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1:
- Minimum 2 disks.
- Good performance ( no striping. no parity ).
- Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ).
RAID LEVEL 5
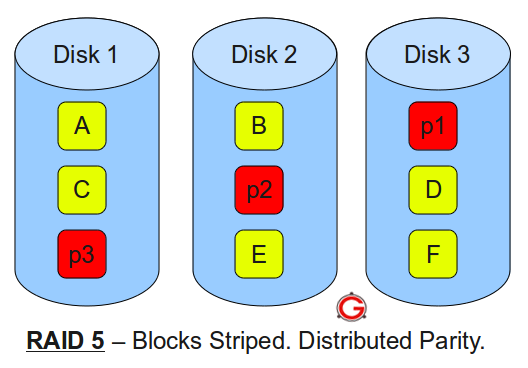
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 5:
- Minimum 3 disks.
- Good performance ( as blocks are striped ).
- Good redundancy ( distributed parity ).
- Best cost effective option providing both performance and redundancy. Use this for DB that is heavily read oriented. Write operations will be slow.
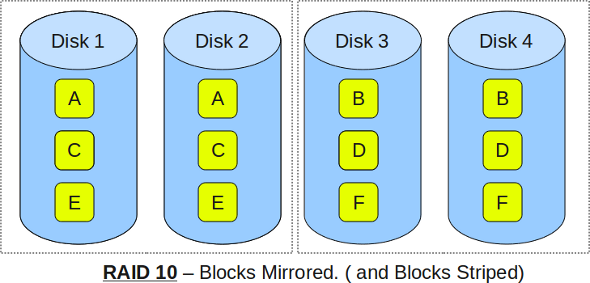
RAID LEVEL 10
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 10:
- Minimum 4 disks.
- This is also called as “stripe of mirrors”
- Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored )
- Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped )
- If you can afford the dollar, this is the BEST option for any mission critical applications (especially databases).
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On Mimastech, You Should Consider:
- Stay Connected to: Facebook | Twitter | Google+
- Support us via PayPal Donation
- Subscribe to our email newsletters.
- Tell other sysadmins / friends about Us - Share and Like our posts and services
We are thankful for your never ending support.



[…] you are new to this, make sure you understand how RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 5 and RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 6 […]
[…] most critical production servers, you will be using either RAID 5 or RAID […]