Introduction to Server Virtualization Technology

In this article we will discuss the Server / Hardware virtualization technology, This is a one type of the virtualization technology used in the IT world. We will discuss it’s implementation methods, and advantages, later in another articles we will install and configure KVM virtualization, and Xen virtualization on different Linux systems. So Let’s start.
Definition of Server / Hardware Virtualization
Virtualization is a broad computing term used for running software, usually multiple operating systems, concurrently and in isolation from other programs on a single system. Simply it’s a way for a machine (Host) to run another operating system (guest virtual machines) on top of the host operating system.
Most existing implementations of virtualization use a hypervisor (or virtual machine manager), a software layer or subsystem that runs directly on server hardware, controls hardware and provides guest operating systems with access to underlying hardware. The hypervisor allows multiple operating systems, called guests, to run on the same physical system by offering virtualized hardware to the guest operating system.
There are two types of hypervisor used with Server / Hardware virtualization:
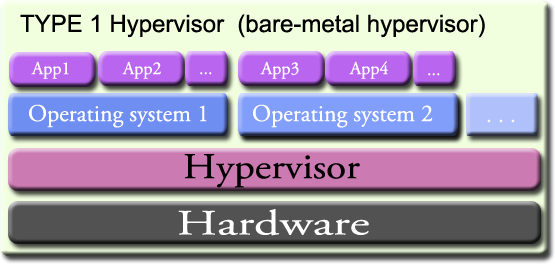
- Type 1: native or bare metal
Native hypervisors are software systems that run directly on the host’s hardware to control the hardware, and to monitor the guest operating systems. Consequently, the guest operating system runs on a separate level above the hypervisor.
Examples of Type 1 hypervisor are Oracle VM, Microsoft Hyper-V, VMWare ESX/ESXI and Citrix XenServer.
The following image shows one physical system with a type 1 hypervisor running directly on the system hardware, and two virtual systems using virtual resources provided by the hypervisor. Each virtual system has it’s own running apps.
- Type 2: hosted
Hosted hypervisors are designed to run within a traditional operating system. In other words, a hosted hypervisor adds a distinct software layer on top of the host operating system, and the guest operating system becomes a third software level above the hardware.
Examples of Type 2 hypervisor are Oracle VM VirtualBox, VMWare Server and Workstation, Microsoft Virtual PC, KVM virtualization, QEMU and Xen virtualization.
The following image shows one physical system with a type 2 hypervisor running on a host operating system and one virtual systems using the virtual resources provided by the hypervisor. The host OS running the hypervisor as an app besides it’s other apps.
Virtualization methods
There are several methods for Server / Hardware virtualiziation, we will focus on the widely used two methods “Full virtualization (FV), and para-virtualization (PV)”. Guest operating systems are hosted on virtual machines using any of these two methods.
- Full virtualization
Full virtualization uses the hardware features of the processor to provide guests with total abstraction of the underlying physical system. This creates a new virtual system, called a virtual machine, that allows guest operating systems to run without modifications. This allows us to run many OSes on the host server. The guest operating system and any applications on the guest virtual machine are unaware of their virtualized environment and run normally.
The Host server must support Hardware-assisted virtualization technology, such as AMD* Virtualization (AMD-V) or Intel* Virtualization Technology (Intel VT). Both Xen virtualization and KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) support full virtualization mode.
- Para-virtualization
Para-virtualization employs a collection of software and data structures that are presented to the virtualized guest, requiring software modifications in the guest operating system to use the paravirtualized environment.
The Host server does not require to support Hardware-assisted virtualization technology. Typically, operating systems running in para-virtualization mode enjoy better performance than those requiring full virtualization mode. Xen virtualization supports para-virtualization mode.
Virtualization Capabilities
Virtualization design provides many capabilities to your organization. Virtualization of operating systems is used in many different computing areas. By using virtualization we are capable of doing the following:
Server consolidation: Many servers can be replaced by one big physical server, so hardware is consolidated, and Guest Operating Systems are converted to virtual machine.
Isolation: guest operating system can be fully isolated from the Host running it. So if the virtual machine is corrupted, the Host system is not harmed.
Migration: A process to move a running virtual machine to another physical machine. Live migration is an extended feature that allows this move without disconnection of the client or the application.
Disaster recovery: Virtualized guests are less dependent on the hardware, so disaster recovery is quicker and easier when the systems are virtualized. On a physical system, if something serious goes wrong, a complete re-install of the operating system is usually required, resulting in hours of recovery time. However, if the systems are virtualized this is much faster due to migration ability. If the requirements for live migration are followed, virtual machines can be restarted on another host, and the longest possible delay would be in restoring guest data. Also, because each of the virtualized systems are completely separate to each other, one system’s downtime will not affect any others.
Advantages of Server / Hardware virtualization
Virtualization brings a lot of advantages while providing the same service as a hardware server. First, it reduces the cost of your infrastructure. Servers are mainly used to provide a service to a customer, and a virtualized operating system can provide the same service with almost the same performance as bare metal systems , adding to that the following advantages:
Agility and productivity: Virtualization provides migration capabilities, live migration and snapshots. These features reduce downtime, and bring an easy way to move your service from one place to another without any service interruption.
Extended life for installed software: Older versions of software “legacy software” may not run on newer, bare metal machines directly. However, by running the older software virtually on a larger, faster system, the life of the software may be extended while taking advantage of the performance from the newer system. This saves us extra money for upgrading the legacy software.
Less hardware: You can run several operating system on one host, so all hardware maintenance will be reduced.
Less power/cooling: Less hardware means you do not need to invest more in electric power, backup power, and cooling if you need more service.
Less space: Consolidating servers onto fewer machines means less physical space is required. This means the space normally occupied by server hardware can be used for other purposes.
Less maintenance: Using a VM Guest simplifies the administration and maintenance of your infrastructure, less time is spent maintaining the VMs. This means less money being spent on parts and labor.
Summary
In this article we have explained the meaning of virtualization “mainly server / hardware virtualization”, also we have explained the meaning of hypervisor ,and it’s two types. We proceed with the types, capabilities and advantages of the server / hardware virtualization.
I hope this article is good enough for you.
See you in other articles.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On Mimastech, You Should Consider:
- Stay Connected to: Facebook | Twitter | Google+
- Support us via PayPal Donation
- Subscribe to our email newsletters.
- Tell other sysadmins / friends about Us - Share and Like our posts and services
We are thankful for your never ending support.